之前有一篇用 Numpy从零搭建Linear Regression。 想着可以简单的用Pytorch做一下,当然对于Pytorch来说有些大材小用了,一个feature, 一个output,就算是简单的学习了
Import library
1 | |
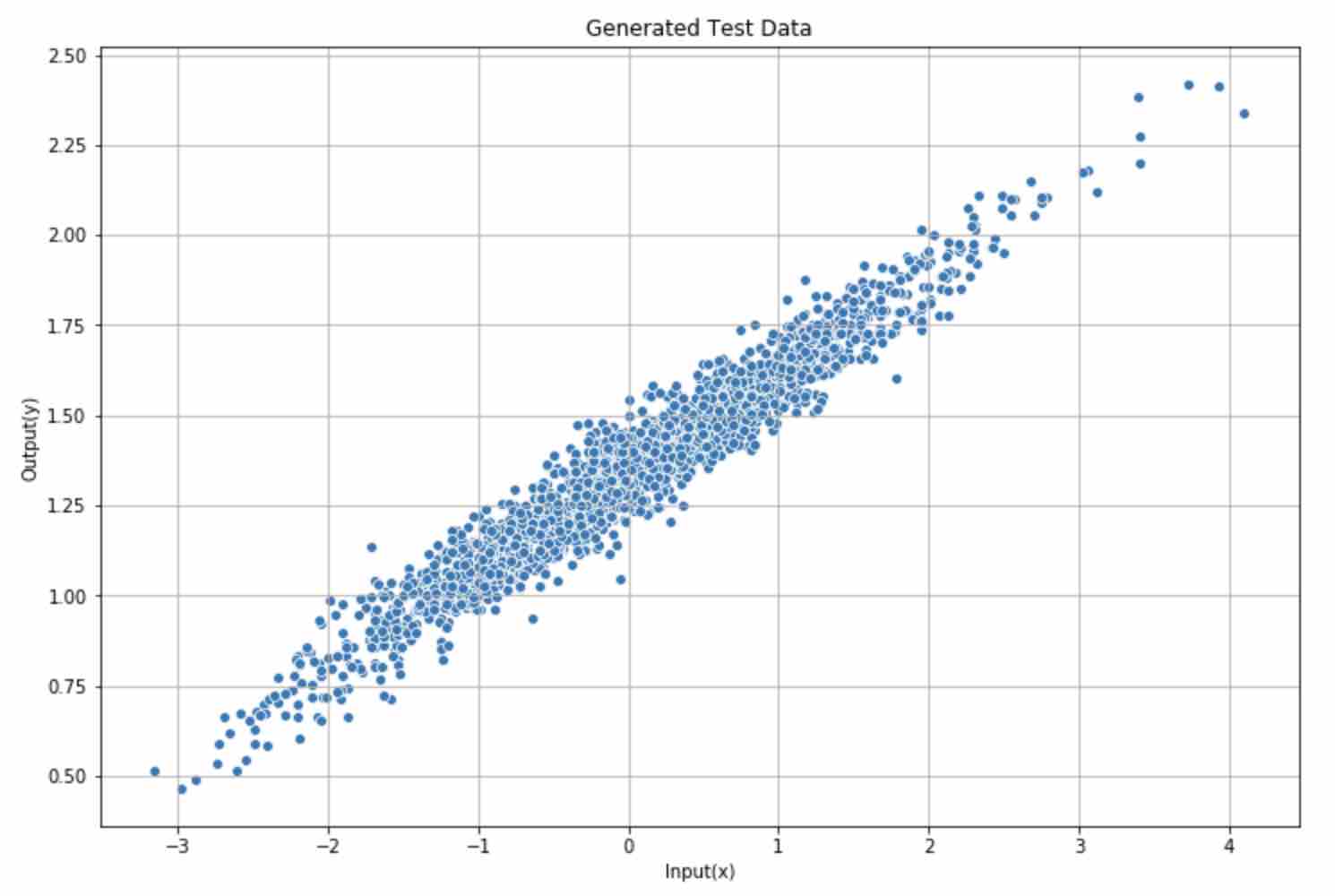
Generate test data
1 | |
Plot generated data
1 | |
Apply Linear model in Pytorch
1 | |
Run model
1 | |
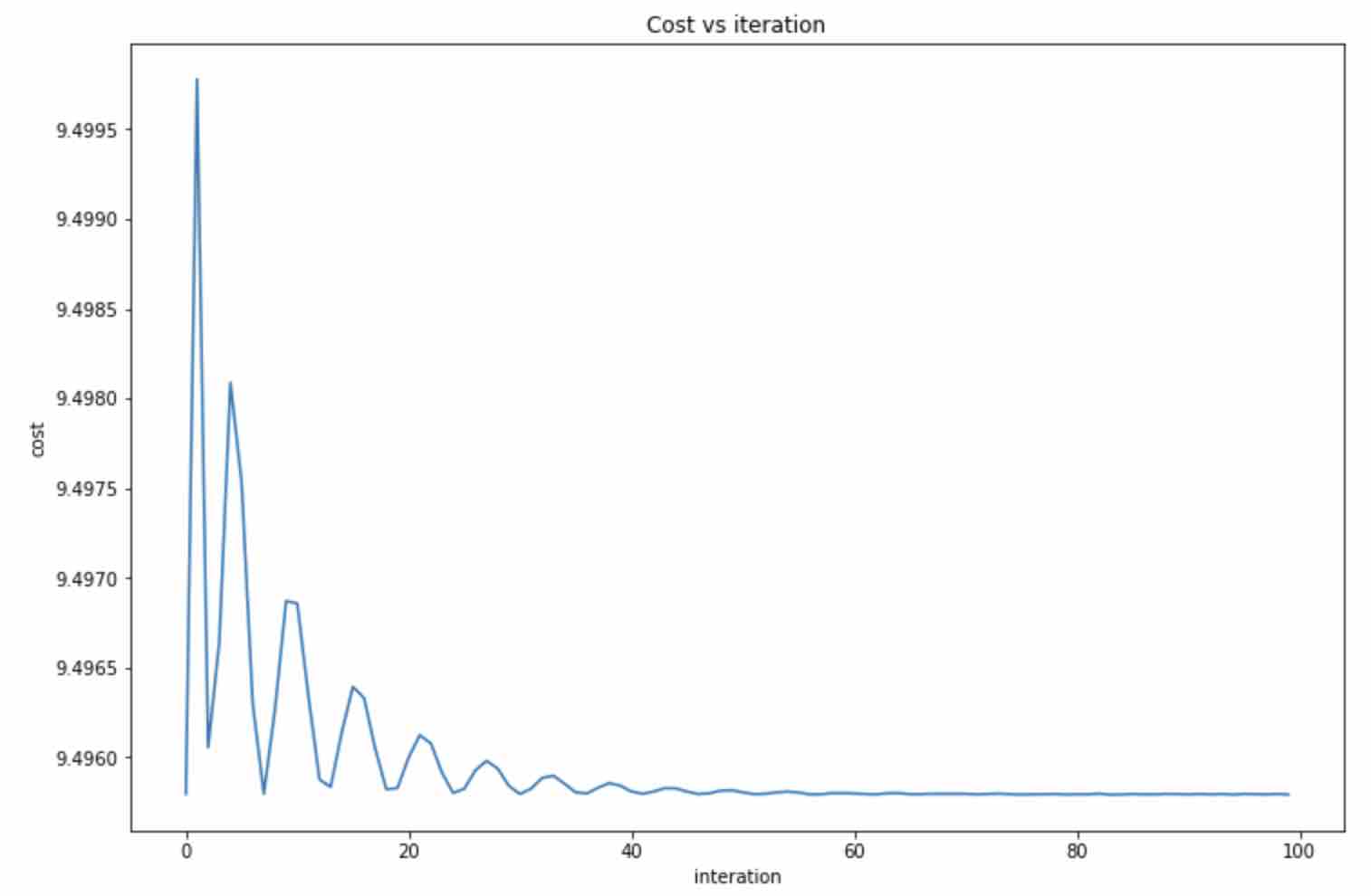
1 | |
Plot predicted linear function
1 | |
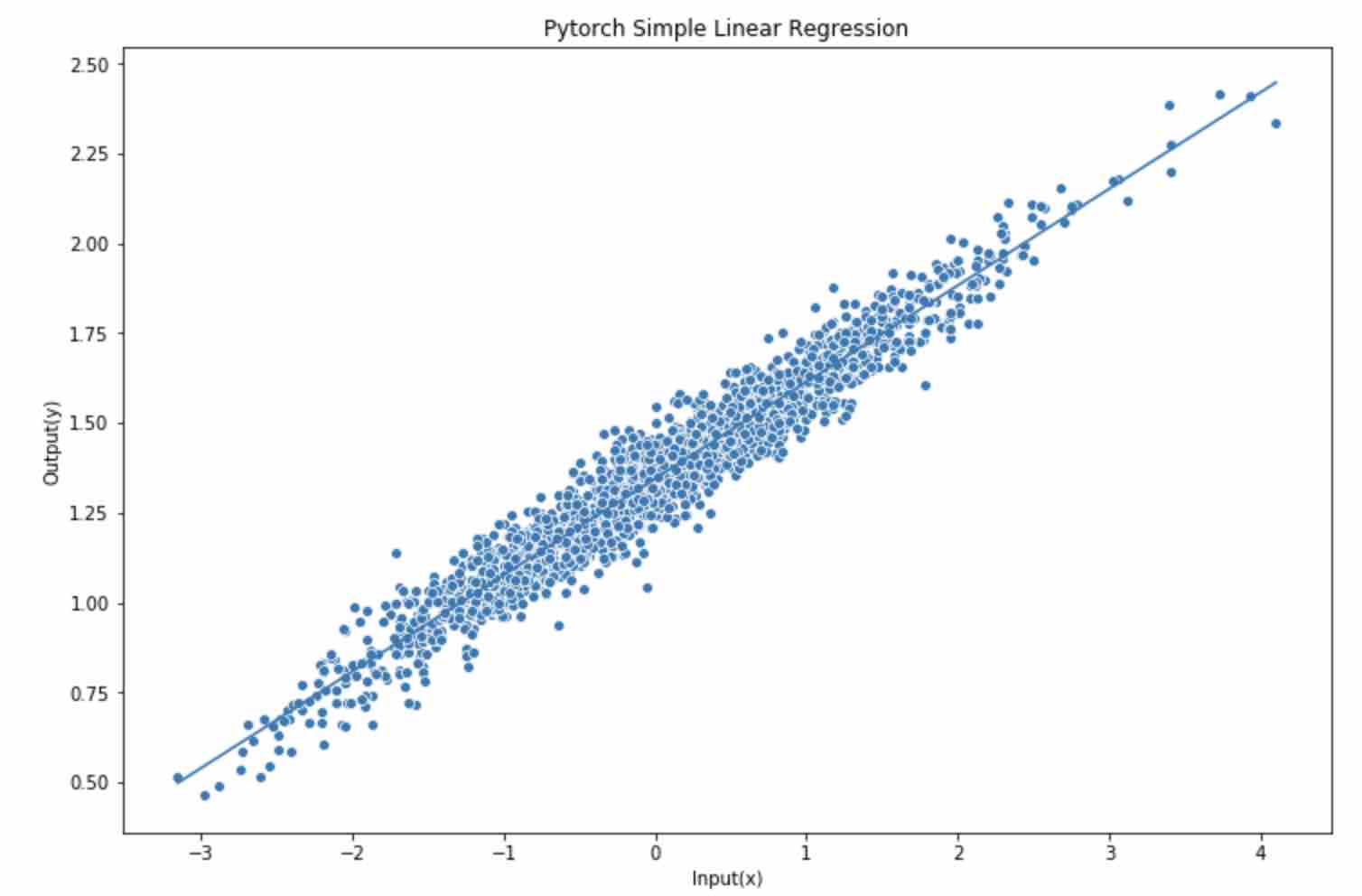
之前有一篇用 Numpy从零搭建Linear Regression。 想着可以简单的用Pytorch做一下,当然对于Pytorch来说有些大材小用了,一个feature, 一个output,就算是简单的学习了
1 | |
1 | |
1 | |

1 | |
1 | |

1 | |
1 | |
